FUE hair transplant definition
FUE Hair Transplant; A popular technique for hair transplantation is called FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction). Individual hair follicles are removed from the donor region and then implanted into the recipient area during a FUE hair transplant.
By removing hair follicles from locations that are not experiencing hair loss and transplanting them to areas where there is baldness or thinning hair, the treatment tries to enhance hair density.
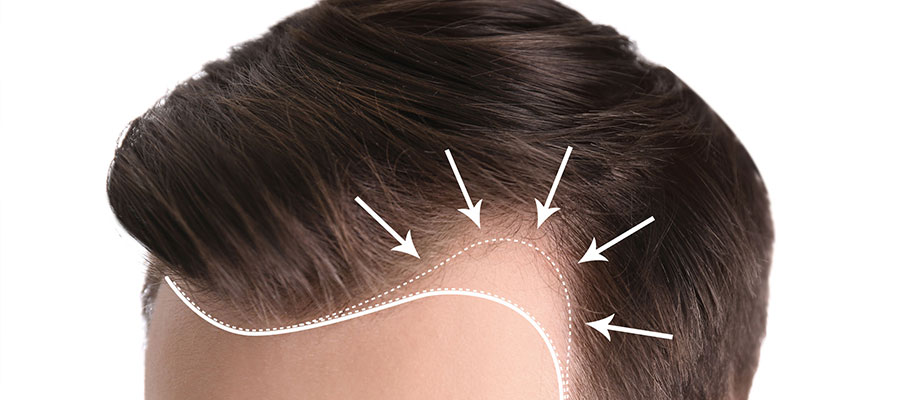
The following stages are a part of the fue hair transplant process: Getting the donor area ready The “donor area” is the region from which healthy hair follicles will be removed. Given that the hair in this location is genetically resistant to thinning, the back of the head is often chosen as the donor area.
To be ready for extraction, the donor area’s hair is cut or cleansed. Hair follicle extraction: Using a specific instrument or technology, hair follicles are individually retrieved from the donor region. Small, dot-like sores may develop after this procedure in the regions where the hair follicles are removed.
Preparation of the recipient region: Tiny incisions or holes are made in the recipient area, which is referred to as the balding or thinning hair areas where the hair transplantation will be performed. The correct positioning of the hair follicles is made possible by these incisions.
To produce a hairline that looks natural, the incisions’ angle and direction are chosen. Hair follicle implantation: The removed hair follicles are inserted into the prepared incisions. The hair follicles are meticulously implanted by the hair transplant expert to provide a natural hairline and a beautiful look.
It’s critical that the hair follicles be positioned correctly in terms of angle and direction. By being exposed to optimal circumstances for new hair development, the implanted hair follicles create a long-lasting bond.
Due to its less invasive nature, the FUE hair transplantation process is often thought to have a quicker recovery period. Careful post-operative monitoring are necessary. Crusting, redness, or some swelling may appear in the transplanted regions, although these conditions usually go away quickly.
In order to improve hair density or stop hair loss, FUE hair transplantation may be used on those who are balding. Both men and women are fans of the surgery. For the following issues, FUE hair transplantation is often preferred: Male pattern baldness is the most prevalent kind of hair loss in males (androgenetic alopecia).
Male pattern baldness may be treated by FUE hair transplantation to correct hair loss or to improve hair density. Hair loss may also affect women, and FUE hair transplantation may be an option to cure hair loss in female pattern baldness or to improve hair density.
Reconstruction of the hairline: A wound, burn, or surgical procedure may cause the hairline to be lost or damaged. A natural hairline may be achieved using FUE hair transplantation. Hair loss or thinning: FUE hair transplantation may boost hair density and provide a fuller-looking hair appearance in circumstances where the hair is typically thin or sparse.
Having a sufficient number of healthy hair follicles in the donor location is a need for FUE hair transplant candidates. If FUE hair transplantation is right for you, a hair transplant expert will evaluate your level of hair loss and the health of the donor area.
How are FUE hair transplants carried out?
The following stages are involved in FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) hair transplantation: Getting the donor area ready The “donor area” is the region from which healthy hair follicles will be removed. Given that the hair in this location is genetically resistant to thinning, the back of the head is often chosen as the donor area.
To be ready for extraction, the donor area’s hair is cut or cleansed. Hair follicle extraction: Using a specific instrument or technology, hair follicles are individually retrieved from the donor region. Hair follicles are removed using microsurgical methods in the FUE procedure. Usually, devices like a manual punch or a tiny motor are utilized. These instruments pierce the tissue covering specific hair follicles, enabling their extraction.
The removed hair follicles are then stored in an appropriate solution. preparing the recipient area: The regions that will get the hair transplantation and have hair loss or thinning hair are referred to as the recipient areas. To make incisions or holes for the hair transplantation, preparation is done. The correct positioning of the hair follicles is made possible by these incisions. The angles and directions needed to produce a natural hairline are decided by the hair transplant expert.
Hair follicle implantation: The removed hair follicles are inserted into the prepared incisions. The hair follicles are meticulously implanted by the hair transplant expert to provide a natural hairline and a beautiful look. It’s critical that the hair follicles be positioned correctly in terms of angle and direction. The hair follicles are exposed to ideal circumstances for new hair development during the implantation stage.
A less invasive process, FUE hair transplantation is often carried out under local anesthetic.
What is the time frame for FUE hair transplantation?
The quantity of grafts to be transplanted, the degree of hair loss, and other variables might affect how long a FUE hair transplant takes. The FUE hair transplantation method may typically take anything from a few hours to several days. The quantity of grafts that need to be transplanted affects how long the surgery takes.
For instance, increasing the quantity of transplanted grafts may be necessary to get a more complete hair density, which might lengthen the surgery. The extent of hair loss, the state of the donor region, and the size of the recipient area are other variables that might influence the length of the treatment.
FUE procedure or Dhi?
There are benefits and contrasts between the two common hair transplantation techniques, FUE and DHI. Your particular case of hair loss, your hair’s features, and your personal preferences will determine which technique you choose. The following are some distinctions between FUE and DHI: Hair follicles are harvested one at a time from the donor region using the FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) technique.
The recipient region is subsequently treated with the transplanted hair follicles. The minimally invasive technique is usually carried out while the patient is under local anesthetic. The length of the process varies according to the quantity of grafts. Usually, the healing process is finished in a few days.
In the donor region, there can still be tiny, dot-like scars. To attain a high hair density, many treatments could be necessary. It is often seen as a more economical choice. Direct Hair Implantation (DHI) involves implanting hair follicles directly into the recipient region. The hair follicles spend less time outside the body while using the DHI procedure.
The method makes use of specialized tools and procedures. With the implanted hair follicles, a more natural appearance is the goal. Compared to FUE, the technique often takes more time. In general, the recuperation procedure and outcomes are comparable to FUE. Small scars might appear, however they usually blend in. Depending on the quantity of grafts, one session can be enough.
How often may hair transplants be done?
The potential for several hair transplant procedures relies on a variety of variables, including the severity of the patient’s hair loss, the quality of the donor area, the size of the recipient region, and the patient’s objectives. In general, hair transplantation may be done over the course of many sessions.
This sum, meanwhile, might differ from person to person. The quantity of hair follicles in the donor region, the level of hair loss, and the desired result of the transplant all have a role in how many hair transplantations a person will have. A specific number of grafts may be transplanted in each session, and further sessions could be required.
A hair transplant expert will assess your level of hair loss and learn about your objectives to choose the best hair transplanting strategy for you. This plan will outline how many grafts must be implanted, how many sessions are necessary, and how long must pass between treatments.
The proportion of transplanted hair that grows varies from person to person and is influenced by a number of variables. These variables include the type of transplantation, the region of the transplant, the caliber of the donor area’s hair follicles, the appropriate use of surgical methods, the patient’s health, and adherence to post-operative care guidelines.
The majority of the transplanted hair follicles will typically develop when the hair transplantation process is carried out effectively and the necessary care is given. The success percentage of hair follicle survival might increase to up to 90% with an experienced hair transplant expert using the right procedures.
However, not all transplanted hair follicles could live in particular circumstances. After transplantation, certain hair follicles may not adjust or they could fall out. This is seen as an expected stage of the healing process. Therefore, it’s crucial to give yourself a few months to witness the full effects and assess hair growth after transplantation.
When after hair transplantation is the transplanted region safe to be touched?
It is often advised to avoid touching the transplanted region during the first few days after hair transplantation. The survival of hair follicles in their new site and good healing both depend on careful management. Following the surgery, you should avoid contacting the transplanted region unless absolutely necessary.
Don’t touch in the early days: After the hair transplant process and during the first few days, it is advisable to avoid touching the transplanted region. Follow your hair transplant specialist’s advice during this period and try to keep your hands as far away from the region as possible.
Adopt the proper post-operative care: It’s crucial to adhere to your doctor’s post-operative care instructions. Be careful when handling the transplanted region throughout this procedure, which may entail cleaning, letting scabs to come off naturally, taking recommended drugs, and sticking to other suggestions. Allow scabs to naturally fall off: After surgery, scabs may develop.
The hair follicles that were transplanted are shielded by these scabs. The scabs are supposed to naturally fall off, thus they should be left alone to do so without assistance. Prevent rubbing or impact on the transplanted area: For the first several weeks, avoid impact or friction on the transplanted region. Be careful, particularly while engaging in risky activities like sports, using tight headgear or accessories, or brushing your hair.
Avoid doing anything that can endanger the transplanted area. Observe your doctor’s recommendations: The directions provided by your hair transplant professional must be properly followed.
They will provide you detailed instructions on how to care for yourself after surgery and how to recuperate. Following these recommendations may have a favorable effect on the outcome of the transplant and the healing process.
Why doesn’t hair transplantation stick?
Several causes may be blamed for low hair follicle survival or hair transplantation failure. Here are some potential explanations for why hair transplantation could not be successful: Unsuitable donor area: The donor region, which is normally resistant to hair loss, is where hair follicles utilized for transplantation are typically taken.
However, inadequate hair follicle survival may occur if the donor area’s hair follicles are of insufficient quality or condition. inadequate nutrition: Healthy hair follicle development depends on proper nourishment. Weak hair follicles and low survival are two consequences of inadequate nutrition. Unsafe surgical procedure: Hair transplant treatments need for the adoption of safe surgical methods.
The survival of hair follicles might be significantly impacted by procedures carried out by unskilled or inexperienced personnel. Failure to follow the recommended healing protocol: After hair transplantation, a thorough healing procedure is essential. Hair follicle survival may be hampered if guidelines are not followed.
Poor survival might result from actions like aggressively removing scabs or exposing the transplanted region to impact or friction. Infection or inflammation: Infection or inflammation that may develop after hair transplantation may impact the survival of hair follicles.
Reduce the risk of infection by practicing proper hygiene and using antibiotics as directed. Hair loss is often caused by hereditary conditions. Hair follicles in the transplanted location could be genetically predisposed to low survival.
How can transplanted hair grow more quickly?
To encourage quicker development of transplanted hair, there are a number of criteria and considerations. Here are some ideas for accelerating hair growth after transplantation: Follow the right healing procedures: It’s critical to follow your doctor’s recommendations for post-operative care. This entails maintaining the transplanted area’s cleanliness and hygiene standards, letting scabs naturally peel off, and taking any recommended drugs on a regular basis.
Faster hair growth is facilitated by maintaining a healthy skin environment throughout the healing process. Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Hair growth is significantly influenced by general health. Faster hair follicle development may be promoted by eating a balanced diet, getting enough water, exercising often, and controlling stress.
Use healthy hair care techniques: For transplanted hair follicles to develop healthily, proper hair care is essential. This entails washing your hair gently, using the proper shampoos and hair products, massaging your scalp to promote blood flow, and shielding your hair from harsh chemicals and heat.
Take a nutritional supplement: Some foods include vitamins, minerals, and proteins that promote hair development. It’s crucial to get these nutrients as part of a balanced diet. Additionally, taking vitamins that promote hair growth on your doctor’s advice might be advantageous.